Can you imagine a Geographical Information System (GIS) for a city like Pune or Mumbai? The city GIS of these cities are crafted by the urban development departments using data from the Municipal Corporation Councils and the Metropolitan Regional Development Authorities like PMRDA, MMRDA, all folding into it. GIS starts with an intelligent map. The municipal corporation provides over 18-20 services to citizens. This includes water supply, sewerage, solid waste collection, road construction, street lights etc. The municipal corporation essentially builds capacities and oversees operations.
In many municipalities, GIS was not adopted at a fully functional level till the Smart Cities initiative. In the last five years, the scenario has changed and many have started adopting GIS. Indian cities earlier did not have a standardised base map, with multiple layers of data on roads, water supply, water distribution etc.
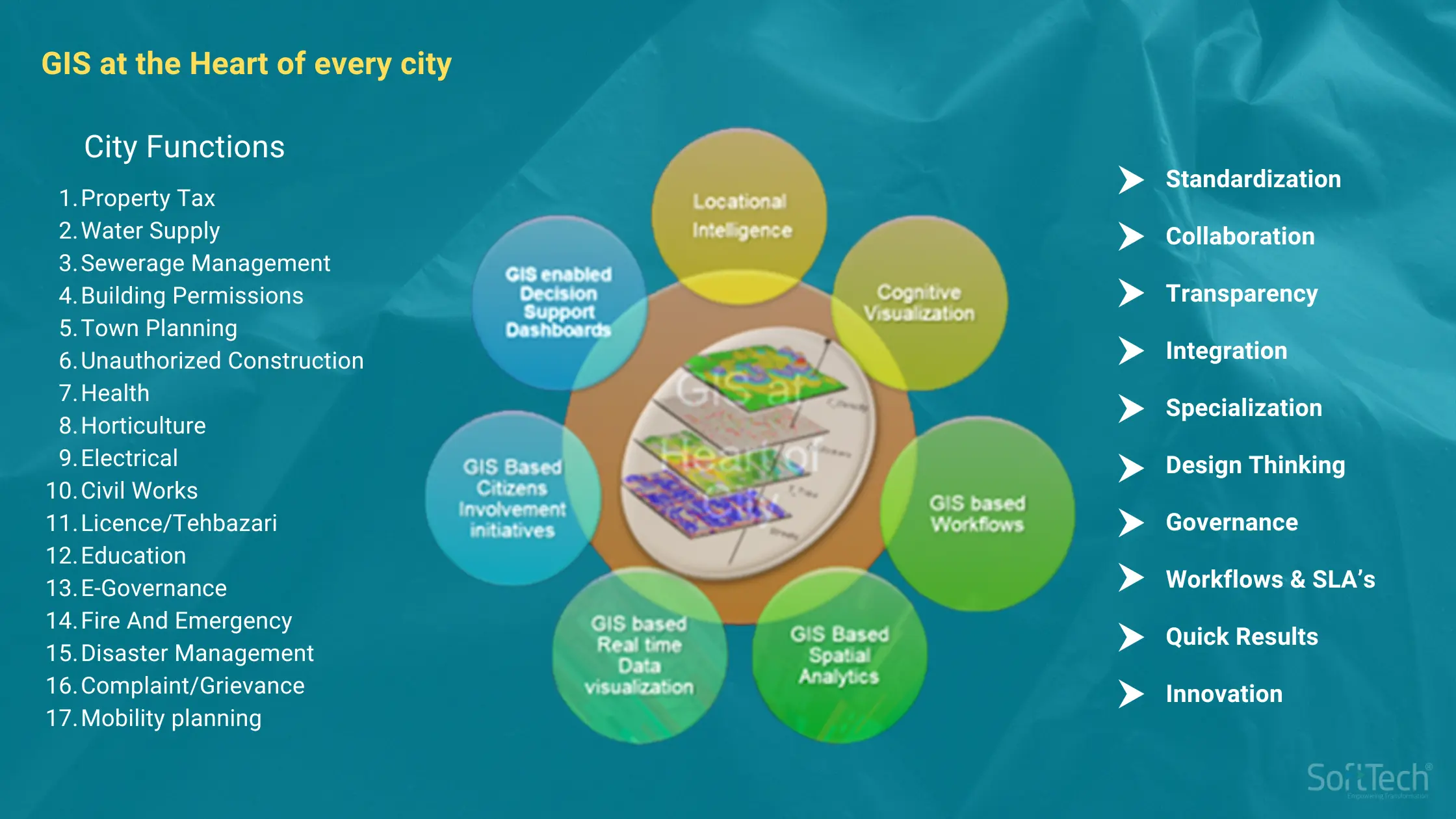
GIS plays a very crucial role in dealing with a large area of many square kilometres with multiple utilities or services which the municipal corporation provides to citizens. Standardisation, collaboration, transparency, integration, specialisation, design thinking; all play a crucial role. Data related to various departmental functions is procured to start the GIS project. This geo-located data with latitude and longitude is normally procured through multiple processes, including ground surveys, mobile apps and even marketing data. Therefore, with GIS, every data point will always have some latitude and longitude to pinpoint it to the earth or to maps.
Paper to Online: Most departments have various paper format data from the pre-computerisation era. These are scanned and put in a digital format for use in GIS maps. Take a land record department, for instance. It has paper data, CAD and GIS data. This is supplemented with data from ground surveys. Nowadays drones capture images too. Drones and satellites are the two major sources of imagery.
Satellite images have been around since the last 30 to 35 years for the various parts of the earth. This is now merged with the physically collected drone or survey images. They are merged to create a high quality single image for the entire city or the area of interest. This photogrammetrically derived product is a digital surface or digital terrain model. These are required by various engineering departments to estimate where the high or low elevation point is, while designing cities, various utilities etc. Then features are created, digitising houses, roads etc with various layers, marked in different colours. These are useful for analysis, layer by layer.
Colour coding: The symbology of buildings is marked with a different colour to say, road projects. This then becomes the final base map, with every attribute mapped onto it. So when a user clicks on the house, he or she will get information on who is the owner, what is the area in square feet, when the property taxes have been paid and so on. These are called attribute linkages.
This is where the GIS is very crucial. Once the relational database management systems are created, users or city officials can query who is staying in the unit, build queries, who has not paid the taxes, etc. This smart digital network allows the management of city data systems to improve efficiency.
GIS technology is transforming urban management, making cities smarter, more efficient, and better equipped to serve their citizens. Ready to harness the power of GIS for your city? Read how SoftTech’s GIS Services can help and start integrating data for smarter solutions today!